

The CREATE TABLE statement accepts foreign key options, when using the It also will have no support for foreign key constraints while INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE statement referring to this table will be invoked asĪutocommit. Of MyISAM will be essentially non-transactional, meaning any
That is created in a MySQL / MariaDB database with a storage engine The InnoDB engine is typically preferred for its support To MyISAM for this value, although newer versions may be defaulting Historically, MySQL server installations would default The most common argument is mysql_engine, which refers to the storageĮngine for the table. Mysql_character_set) and INDEX DIRECTORY (e.g. mysql_data_directory), CHARACTER SET (e.g. These particular names, which include DATA DIRECTORY Instead of an underscore to support this, the MySQL dialect has awareness of A handful of these names will render with a space

Mysql_keyword_name to be rendered as KEYWORD_NAME in theĬREATE TABLE statement. The MySQL / MariaDB dialects will normally transfer any keyword specified as # support both "mysql" and "mariadb-only" engine URLs Table ( 'mytable', metadata, Column ( 'data', String ( 32 )), mysql_engine = 'InnoDB', mariadb_engine = 'InnoDB', mysql_charset = 'utf8mb4', mariadb_charset = 'utf8', mysql_key_block_size = "1024" mariadb_key_block_size = "1024" )
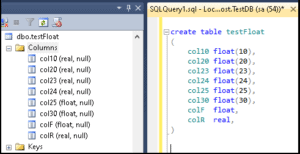
Mysql float update#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
